Working: 8.00am - 5.00pm

Small and Medium Enterprises in Malaysia
SMEs in Malaysia
In the context of Malaysia, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are critical to the country's economy, playing a significant role in job creation, innovation, and economic growth. SMEs in Malaysia are defined based on criteria set by the National SME Development Council (NSDC), which considers both annual sales turnover and the number of full-time employees.
Definition of SMEs in Malaysia
Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of the Malaysian economy since they are the largest category of business in the country and, as such, provide paramount contributions. However, referring to the past studies on SMEs in Malaysia from 2001 to the most recent (2020) studies, it was found that SMEs faced various issues, challenges, and hindrances, thus preventing the growth of their operations. Many SMEs also have problems ensuring their sustainability as well as remaining competitive in the market and changing environment. SMEs in Malaysia are categorized into two broad sectors: Manufacturing and Services & Other Sectors
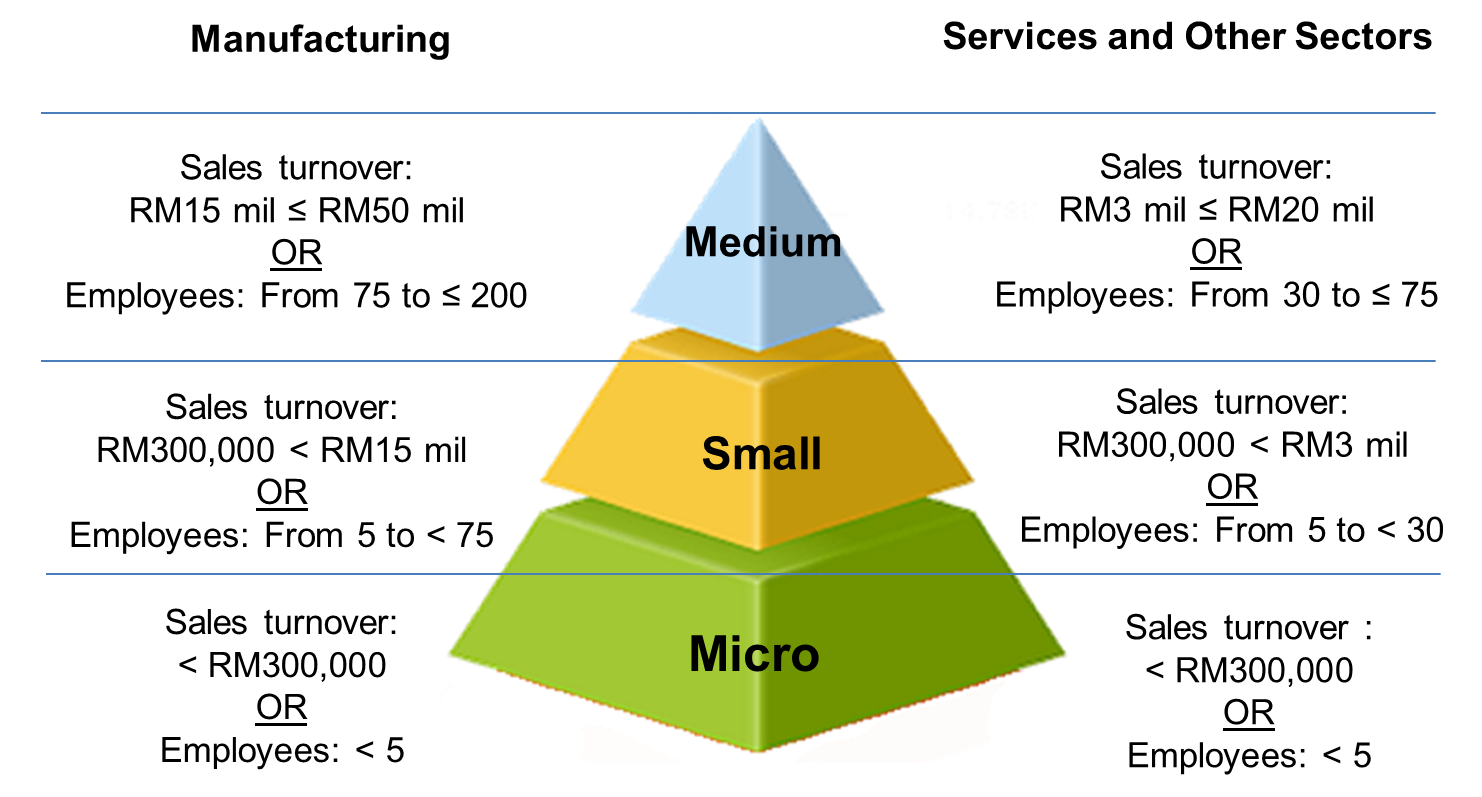
Manufacturing Sector:
Small Enterprises:
Annual Sales Turnover: RM 300,000 to less than RM 15 million
Number of Employees: Between 5 and 75 full-time employees
Medium Enterprises:
Annual Sales Turnover: RM 15 million to not exceeding RM 50 million
Number of Employees: Between 75 and 200 full-time employees
Services & Other Sectors:
Small Enterprises:
Annual Sales Turnover: RM 300,000 to less than RM 3 million
Number of Employees: Between 5 and 30 full-time employees
Medium Enterprises:
Annual Sales Turnover: RM 3 million to not exceeding RM 20 million
Number of Employees: Between 30 and 75 full-time employees
“According to SME Annual Report in 2017/2018, annual growth of SME GDP by economic sector registered a growth of 7.3% (agriculture), 8.9% (quarrying and mining), 6.8% (manufacturing), 6.6% (construction), 7.3% (services). ”
SME Corp
Author
SMEs in Malaysia contributed 5.2% of National Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth in 2016, with 36.6% SME’s contribution to the country’s GDP (SME, 2017). Given that SMEs performance is linked with the domestic demand, Malaysian government is committed towards creating a conducive business environment for Small Medium Enterprise (SME). Furthermore, the job market is squeezed, resulting individual to involve in entrepreneurship. Lately, the world is facing high education unemployment and government has encouraged them to become an entrepreneur as one of the solutions as the source of income.
Based on SME Corporation, detailed definition of the category, namely micro, small, and medium is as follows:


The Main Challenges of Malaysia SME
Small and medium enterprise (SMEs) in the Malaysian economy, play a vital role in the country' economy. They are considered the backbone of industrial growth. In Malaysia, 32% of the country’s gross domestic product comes from SMEs. This is a huge boost for the country’s economy as it shows that the resilient SMEs sector is an integral part of the economy. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Malaysia face several challenges that can hinder their growth and sustainability. Here are the main problems that SMEs in Malaysia commonly encounter:

Limited Access to Credit
Complex Regulatory Environment
Slow Digital Adoption
Intense Competition
Lack of Branding and Marketing
These problems highlight the various obstacles that SMEs in Malaysia must overcome to thrive in a competitive and rapidly changing business landscape. Addressing these challenges requires targeted support from the government, financial institutions, and industry associations.

